RMF Implement
CGRC ·NIST Risk Management Framework
RMF Implement
This is the series of articles to use as a study guide for the (ISC)2 CGRC exam. In this article, we will discuss the Implement steps in the Risk Management Framework.
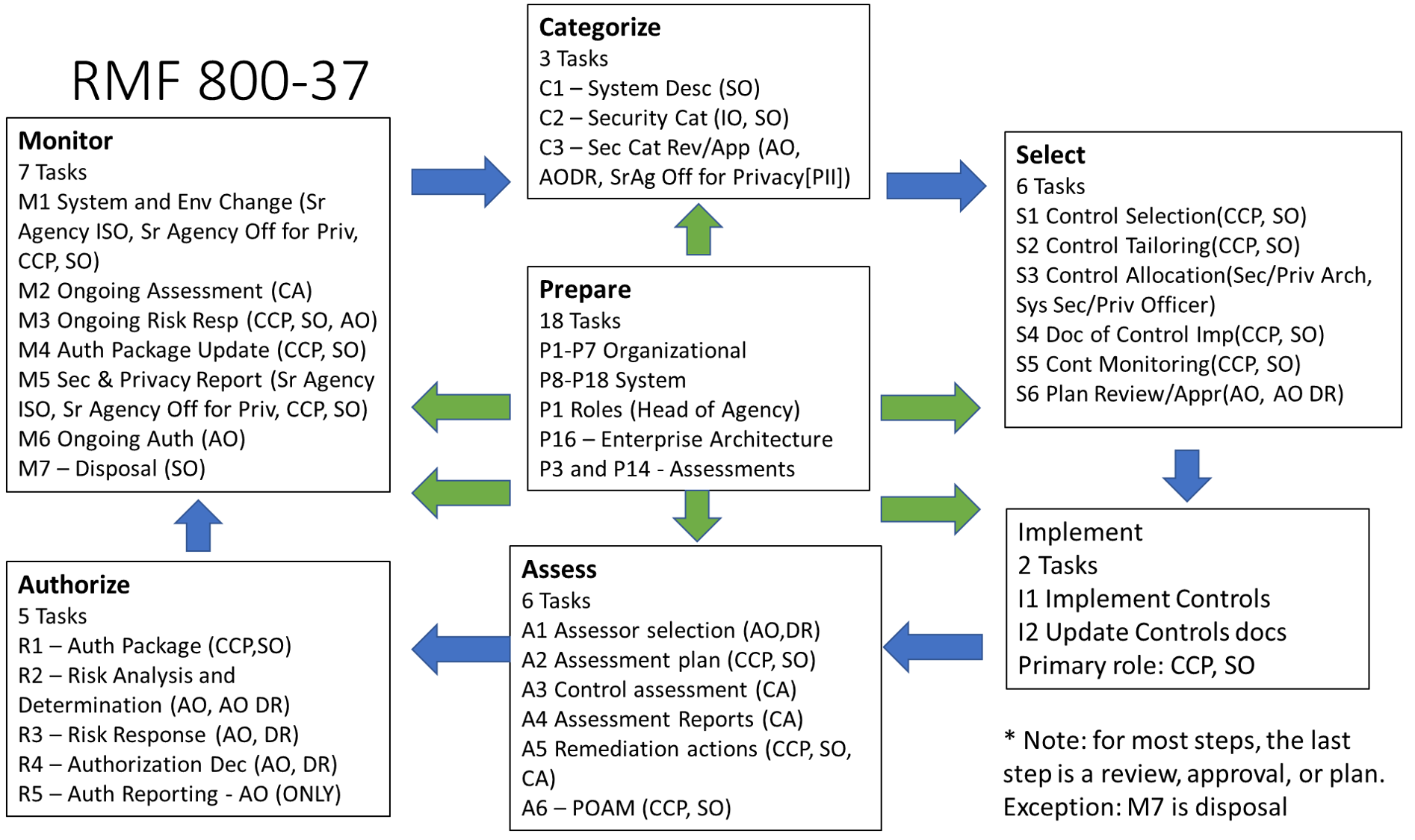
Implement Tasks
- I-1 – Control Implementation
- I-2 – Update Control implementation information
- Primary roles for both – CCP and SO
Implementation Standards and Guidelines
- 800-37
- 800-34 – Contingency planning guide
- BCP – Business continuity plan
- COOP – Continuity of Operations plan
- Crisis Communications plan
- Critical infrastructure protection plan
- Cyber Incident Response plan
- DRP – Disaster recovery plan
- Information system contingency plan (ISCP)
- Occupant emergency plan (OEP)
- 800-128
- Configuration management
- Configuration item
- Baseline configuration
- Configuration management plan
- Configuration control board (CCB)
- 800-128 SecCM (Security focused configuration management)
- Planning
- Identifying and implementing configurations
- Controlling configuration changes
- Monitoring
- 800-70 Checklist Process
- Defense Information Security Agency Security Technical Implementation Guides (DISA STIG)
- CIS Control benchmarks
- Offense informs defense
- Prioritization
- Measurements and metrics
- Continuous diagnostics and mitigation
- Automation
- CIS has over 140 configuration guidelines
- FIPS 140-2
- CAVP – cryptographic algorithm
- CMVP – cryptographic module
- 800-160 – security design principles
Implement Task Details
- I-1 – Control Implementation
- Input – Enterprise architecture, approved security and privacy plans, system design documents, BIA, organizational security and privacy policies and procedures, security and privacy architecture information, system element information, system component inventory, risk assessment results.
- Output – Implemented controls
- Primary role – CCP and SO
- Related tasks – S4, P3, P10, P14, P15, P16, P17
- SDLC – development/acquisition
- National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP)
- Common criteria
- NIST Cryptographic Module Validation Program (CMVP)
- Compensating control – in lieu of baseline controls
- Supplementary control – additional controls or control enhancements
- I-2 – Update Control implementation information
- Input – security and privacy plans, information from control implementation efforts
- Output – security and privacy plans updated with implementation detail sufficient for use by assessors, system configuration baselines
- Primary role – CCP and SO
- Related tasks – S4, I1
- SDLC – development/acquisition
